Tupper's Self Referential Formula in R
Abstract:
We implement Tupper’s self-referencing formula in R. This has been done before by others, but the joy was to be able to learn how to do it yourself using the tidyverse.
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. The R-markdown
source code of this blog is available under a GNU General Public
License (GPL v3) license from GitHub.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. The R-markdown
source code of this blog is available under a GNU General Public
License (GPL v3) license from GitHub.
Introduction
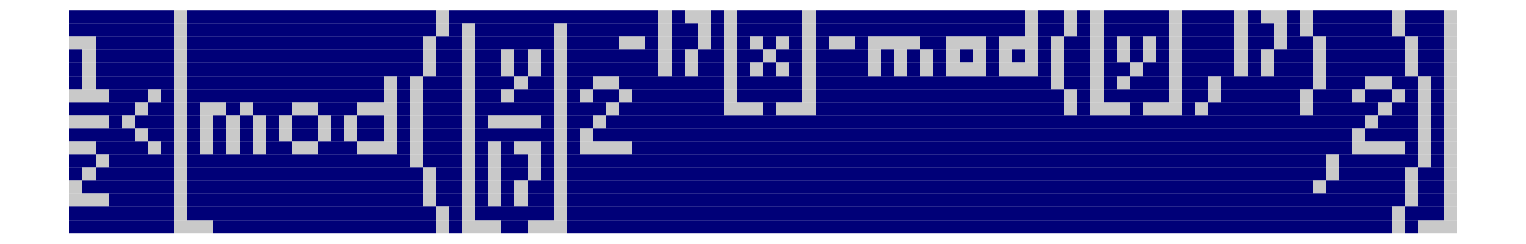
Tupper’s self-referencial formula (Tupper 2001) is an equation which maps a 2D \((x,y)\) coordinate to an \(\{\text{FALSE},\text{TRUE}\}\) value. If \((x,y)\) represent pixel locations, the output over a grid of values can thought of as a black & white image where the true/false values are mapped to \(\{0,1\}\) in the usual way. Tupper’s formula is \(f(x,y) =\) \[ \frac{1}{2} < \left\lfloor \operatorname{mod}\left( \left\lfloor\frac{y}{17}\right\rfloor\cdot 2^{-17\lfloor x \rfloor - \operatorname{mod}(\lfloor y \rfloor, 17)}, 2\right)\right\rfloor. \] We note that if one evaluates the function for all integers \((x,y)\) for \(0 \leq x \leq 105\) and \(k\leq y\leq k+16\), where \(k\) is a fixed constant, then one gets a binary image with 106x17 pixels. The entire magic of Tupper’s formula is that it’s just unpacking an encoding of that 106x17 grid by representing it as a 1802 long binary number which is then converted from base-2 into base-10. For some (not so obvious) reason this number is then multiplied by 17 to yield the final value of \(k\) (in base-10)1.
We also note that since the right-hand side of Tupper’s equation will always be 0 or 1, the comparison with \(\frac{1}{2}\) appears superfluous and seems to be just a way to get a Boolean instead of a 0/1. Furthermore, since we will be using only integer values for \(x\) and \(y\), the floor operators around \(x\) and \(y\) are not really needed either.
More Background
Initially, I learned about the formula from a twitter post:
Tupper's self-referential formula is a formula that visually represents itself when graphed at a specific location in the (x, y) plane. pic.twitter.com/wAUVahJ9Dq
— Fermat's Library ((fermatslibrary?)) February 4, 2018
A nice Numberphile video has also been dedicated to the formula.
R Implementation
One challenge of implementing Tupper’s formula in R is that \(k\) will be a very large integer (~500
digits). Hence, one needs a special purpose library to handle these
large numbers. StaTEAstics in their 2013 R
blog post on Tupper’s formula use the GNU Multiple Precision
Arithmetic Library for this purpose and is interfaced in the gmp
R package. We follow their implementation:
## GNU Multiple Precision Arithmetic Library) for handling the long integers
library(gmp)
## Define the constant k
k <- as.bigz("960939379918958884971672962127852754715004339660129306651505519271702802395266424689642842174350718121267153782770623355993237280874144307891325963941337723487857735749823926629715517173716995165232890538221612403238855866184013235585136048828693337902491454229288667081096184496091705183454067827731551705405381627380967602565625016981482083418783163849115590225610003652351370343874461848378737238198224849863465033159410054974700593138339226497249461751545728366702369745461014655997933798537483143786841806593422227898388722980000748404719")Thus an R function implementing Tupper’s formula is:
tupper <- function(x, y, k) {
z1 <- as.bigz(y + k)
z2 <- as.bigq(floor(z1/17))
z3 <- 2^(-17 * floor(x) - as.bigz(floor(z1) %% 17))
return(0.5 < floor(as.bigz(z2 * z3) %% 2))
}Here we have used \(k\) explicitly in order to have \(y\) run from 0 to 16, which is easier for the subsequent plotting. Applying the R function to an appropriate grid of values (and reversing the index directions to account for the horizontal plotting direction):
im <- expand_grid(x=0:105L, y=0:16L) %>%
rowwise() %>%
mutate(z=tupper(105-x, 16-y, k=k))The result can then easily plotted:
plot_tupper <- function(im, palette=c("darkblue", "lightgray")) {
ggplot(data=im, aes(x=x,y=y,fill=as.factor(z))) + geom_tile() +
scale_fill_manual(values=palette) +
theme_void() +
theme(legend.position="none") +
coord_equal()
}
plot_tupper(im)
Behind the Scenes
To check the underlying binary representation we convert \(k/17\) to base-2 notation. However, the multiplication by 17 (10001 in base-2) not only ensures that taking \(k\) modulo the height of the image starts at zero, but it is also helpful to keep possible trailing zeroes in the encoding of the image. Since we know the image size has to be \(17\times 106=1802\) we simply fill the trailing zeroes, if the base-2 converted result of \(k/17\) does not have a length of 1802.
Convert to base-2 number of length 1802 and visualize the number:
char <- as.character(k/17, b=2)
## Add trailing zeroes, which are missing coz the first two pixel are 0.
char <- str_c(str_c(rep("0",17*106 - str_length(char)), collapse=""), char)
cat(char)00110010101000100001010101011111000010010010100000000000000000000000000000001000000000000000101000000000000010001000000000000000000000001111111111111111110000000000000000100000111100000000000000001000000000000011100000000000000000100000000000001110000000000000000000000000000000011000000000000001001000000000000010010000000000000011000000000000000000000000000000001100000000000000100100000000000001001000000000000011111100000000000000000000000000011111110000000111000000011100110000000000000110000000000000000011111111111111110100000000000000001011111010000000000000000101011000001100101001000001000111010001100010000000000000000111111111111111100000000000000000000000011001000000000000101001000000000001001010000000000010001000100000000000000001000000000000000000000000000000011111000000000000000000000000000001100100000000000000111000000000000000000000000001111111100000000010000000000000000100101000000000000000100000000000010010100000000000100000000000000001111111100000000000000000000000000000001000000000000000010000000000000000000000000000000111000000000000000010000000000000011100000000000000001000000000000001100000000000000000000000000000000111000000000000001010000000000000011100000000000000000000000000000001110000000000000010100000000000000111110000000000000000000000000000111100000000000110000110000000000000000000000000011111111000000000100000000000000001010110000000000000010000000000000100011000000000001000000000000000011111111000000000000000000000000001000000000000000001100000000000000000000000000000000001111100000000000000000000000000000110010000000000000011100000000000000000000000000110000110001000000011110000001100000000000000000000000000000000001100100000000000010100100000000000100101000001100001000100001100111000000011100100001111111000001000000000000000011111111111111111str_length(char)[1] 1802Shown splitted into chunks of 17 and for better plotting replacing 0 with ” ” and 1 with “█”
char_split <- stri_sub(char, seq(1, stringi::stri_length(char),by=17), length=17)
plot_string <- str_c(char_split, collapse="\n") %>%
str_replace_all("0", " ") %>%
str_replace_all("1", "█")
cat(plot_string) ██ █ █ █ █
█ █ █ █ █████
█ █ █ █
█
█ █
█ █
█████████████████
█
█ ████
█
███
█
███
██
█ █
█ █
██
██
█ █
█ █
██████
███████
███ ███
██ ██
████████████████
█
█ █████ █
█ █ ██
██ █ █ █
█ ███ █ ██
█
████████████████
██ █
█ █ █
█ █ █
█ █ █
█
█████
██ █
███
████████
█
█ █ █
█
█ █ █
█
████████
█
█
███
█
███
█
██
███
█ █
███
███
█ █
█████
████
██ ██
████████
█
█ █ ██
█
█ ██
█
████████
█
██
█████
██ █
███
██ ██
█ ████
██
██ █
█ █ █
█ █ █
██ █ █ ██
███ ███
█ ███████
█
█████████████████or somewhat better visible as a plot:
## Convert to image data.frame
im2 <- expand_grid(x=0:105, y=0:16)
im2 <- im2 %>% mutate(idx = y + (x*17) + 1) %>% rowwise() %>%
mutate(value_str = str_sub(char, start=idx, end=idx),
value = as.numeric(value_str)) ![]() We find the above binary number by starting in the (0,0) cell and
reading upwards in the \(x=0\)
column.
We find the above binary number by starting in the (0,0) cell and
reading upwards in the \(x=0\)
column.
Discussion
Given the entire “magic” of Tupper’s formula is in \(k\), this site allows you to upload a raw 106x17 image and get the corresponding \(k\) for use in the formula. With Gimp’s PBM export functionality it’s thus easy to make your own plotting, e.g. with \(k\) equal to
186884211780601757089521467754254266534847988959618908270134320886923032590936706609566110951773945064529540811157829398942842590351995031478543240582993263095682288889081666401727057238884719133521833705371096422637085577259001963761107220646739852199923964701689237214047197937015515747842387117086366819859986916183575585602891273928856883765838042528273754853751383296206633974324557163987001300322007312244691824532706662875082651525203923748809153375012301876787226286483554151163460581654755346590825663755194466304we get
 Happy self-referential plotting!
Happy self-referential plotting!
Literature
For details about why the multiplication with the height is done, see Arvind Narayanan’s post Tupper’s Self-Referential Formula Debunked.↩︎